Condor Jobs
Table of Contents
- Brief introduction
- Condor Commands Summary
- See interactive running status of a job
- Debug Condor Issue
- Using Main Commands instead of Alias Commands in Condor Jobs
- Some important notes
- Reference
- Few Specific Examples
Brief introduction
Condor is a specialized workload management system for high-throughput computing. It is designed to manage large numbers of jobs, with a focus on efficient use of compute resources and minimizing downtime.
A Condor job is a unit of work that is executed on a compute node in a Condor pool. Jobs can be submitted to a Condor pool, and Condor will manage the execution of the jobs on available resources.
Condor Commands Summary
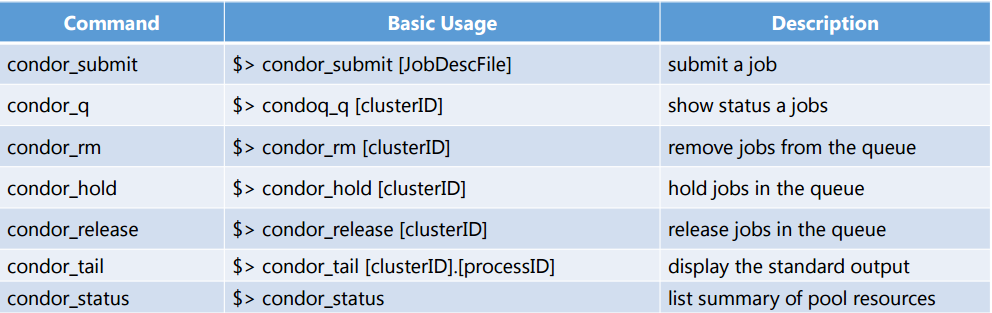
See interactive running status of a job
condor_tail [clusterID].[processID] -f
-
-f: if you want to follow the output and see the updates immediately. - This command is similar to the bash tail -f command.
Debug Condor Issue
Check condor history
- Use the
condor_historycommand to get a list of recently completed job IDs. You can use the following command:condor_history <USER-NAME>- This command will show a list of all jobs that have completed recently, along with their exit status and other information. You can use this information to identify the job IDs of the two completed jobs you are looking for.
- This command can be particularly helpful if you have a large number of submitted Condor jobs, and you need to identify a small subset of jobs that have recently completed.
Check reason for hold/Ideal
If condor job is ideal for long time then before doing anything try to understand why its ideal. Below command will help you in investigating this:
condor_q [job-ID] -analyze
or
condor_q [job-ID] -better-analyze
In case if the jobs remain in ideal state then we can see using this why the status is ideal.
Fix hold without killing job
-
If the job goes to hold because of memory issue then fix it like below:
condor_qedit -name <Name of Scheduler> <cluster>.<proc> request_memory 5000
Using Main Commands instead of Alias Commands in Condor Jobs
When running jobs on the condor system, it is important to note that some commands may not work as expected. In particular, the eos commands or CMSSW commands are not accessible from condor node. This is because the general eos/CMSSW commands are aliases of the main commands. Therefore, in condor jobs, we have to use the main commands instead of the aliases.
For example, the eosls command is an alias of eos root://cmseos.fnal.gov ls. To use eosls in a Condor job, you would need to use the main command instead:
eos root://cmseos.fnal.gov ls <path>
Here is a list of general alias commands and their corresponding main commands:
List below shows general alias and its full command:
| alias | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| eosls | eos root://cmseos.fnal.gov ls | list files placed on EOS |
| cmsenv | eval `scramv1 runtime -sh` | load CMSSW environment |
| cmsrel | scramv1 project CMSSW | Get a particular CMSSW release |
List of condor Queue
| name (Used in condor script) | max duration | name |
|---|---|---|
| espresso | 20min | 8nm |
| microcentury | 1h | 1nh |
| longlunch | 2h | 8nh |
| workday | 8h | 1nd |
| tomorrow | 1d | 2nd |
| testmatch | 3d | 1nw |
| nextweek | 1w | 2nw |
Condor Examples
Ref: http://batchdocs.web.cern.ch/batchdocs/tutorial/exercise1a.html
For condor jobs we have to make two files for job submission. First file is the condor submit descriptor file and another file is the shell script.
Suppose we want to submit the program “Hello_world.cpp” using condor.
-
Cpp program file name:
Hello_world.cpp.{ std::cout << "Hello world..." << std::endl; } -
Condor submitter descriptor file: test.jdl
+JobFlavour = "espresso" # this we need at lxplus not on lpc Executable = test.sh Universe = vanilla Notification = ERROR Transfer_Input_Files = Hello_world.cpp, test.sh x509userproxy = $ENV(X509_USER_PROXY) Output = Condor_LogFiles_$(Cluster)_$(Process).stdout Error = Condor_LogFiles_$(Cluster)_$(Process).stdout Log = Condor_LogFiles_$(Cluster)_$(Process).log Arguments = $(Cluster) $(Process) Hello_world.cpp Queue 1 -
Shell script file: test.sh
#!/bin/bash # I ADDED TOO MANY ECHO STATEMENT JUST TO SEE THE # LOG FILE AND UNDERSTAND. echo "Starting job on " `date` echo "Running on: `uname -a`" echo "System software: `cat /etc/redhat-release`" source /cvmfs/cms.cern.ch/cmsset_default.sh echo "###################################################" echo "# List of Input Arguments: " echo "###################################################" echo "Input Arguments (Cluster ID): $1" echo "Input Arguments (Proc ID): $2" echo "Input Arguments (Config file name): $3" echo "###################################################" # uncomment below line and give path of eos where output need to transfer # OUTDIR=root://cmseos.fnal.gov//store/user/<userName>/ echo "===============================" echo "PWD: "$PWD echo "===============================" echo "== Load CMSSW environment ==" eval `scramv1 project CMSSW CMSSW_10_2_22` # copy file Hello_world.cpp inside the CMSSW directory cp Hello_world.cpp CMSSW_10_2_22/src/ cd CMSSW_10_2_22/src/ # set cmssw environment eval `scram runtime -sh` echo "== Running C++ program =====" echo "===============================" root -l -b -q Hello_world.cpp echo "===============================" echo "xrdcp output for condor" # xrdcp -f outPut_${1}_${2}.root ${OUTDIR}/outPut_${1}_${2}.root # here $1 and $2 is the cluster ID and job ID and it is passed # through the arguments from jdl file echo "===============================" date -
To submit job run the command:
condor_submit test.jdl -
Check the status using:
condor_q -
When job finishes, one can investigate the log files. In the above example it was named as
Condor_LogFiles_*.stdoutandCondor_LogFiles_*.log
Some important notes
-
Don’t execute das queries in batch jobs:
It is not a good idea to execute das queries in batch jobs, because it could overwhelm the database if thousands of jobs send simultaneous requests. Instead, you should execute your cmsDriver.py command locally with the --no_exec option, and then in your job script, do: cmsRun [config] where [config] is the output python config file from cmsDriver.py. -
PROXY ISSUE: At LXPLUS we may have the issue with reading the remote files and the error message will be something like:
Error in <TNetXNGFile::Open>: [ERROR] Server responded with an error: [3011] No servers are available to read the file.To get rid of this we need to map our proxy properly in the condor script. For this follow the following steps: a) After setting proxy do
cp /tmp/x509up_u117617 /afs/cern.ch/user/<NameInitial>/<UserName>/ export X509_USER_PROXY=/afs/cern.ch/user/<NameInitial>/<UserName>/x509up_u117617Here,
/tmp/x509up_u117617is the file as you got while setting the proxy usingvoms-proxy-init --voms cms --valid 168:00Remember to submit jobs from this terminal only
b) In condor jdl file add the following line:
x509userproxy = $ENV(X509_USER_PROXY) -
Switch to the best condor node:
myschedd bump -
Change of schedular at lxplus: If you want to switch to schedular named
bigbird17then use command:export _condor_SCHEDD_HOST=bigbird17.cern.ch export _condor_CREDD_HOST=bigbird17.cern.ch -
Add the system requirement for SL9
Requirements = (TARGET.OpSysAndVer =?= "AlmaLinux9")
Reference
-
Lxplus condor tutorial: link
-
Condor Guide (lxplus): link
-
https://indico.cern.ch/event/366578/sessions/73138/attachments/728847/1000050/LHC_.pdf
-
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/13157442/condor-output-file-updating
-
http://research.cs.wisc.edu/htcondor/manual/v7.6/2_5Submitting_Job.html
-
http://uscms.org/uscms_at_work/computing/setup/batch_systems.shtml
Few Specific Examples
- General script for the condor job: link
- Run MadGraph Jobs through condor
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: